Common
Bookkeeping Accounts
-
Asset Accounts
-
Liability Accounts
-
Equity Accounts
-
Income Accounts
-
Expense Accounts
Common
Bookkeeping Accounts
Bookkeeping involves tracking all
the financial activities of a business, and to do that effectively, you need to
understand the most common accounts used in the Chart of Accounts. These
accounts help categorize income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity in a
way that makes financial reports accurate and meaningful.
“Bookkeeping accounts are specific categories used to organize financial transactions for proper recording and reporting.”
Let’s explore the main types of accounts that appear in almost every business.
“Bookkeeping accounts are specific categories used to organize financial transactions for proper recording and reporting.”
Let’s explore the main types of accounts that appear in almost every business.
1. What Is the General Ledger?
Asset accounts track what the business
owns. Common examples include cash, which
represents money in hand or in bank accounts, and accounts receivable, which is
the money customers owe to the business. Inventory
refers to goods available for sale, while prepaid
expenses include payments made in advance, such as insurance.
Other asset accounts may include equipment or furniture,
which are physical items used in the daily operations of the business. These
accounts increase when the business acquires something of value and decrease
when those assets are either used or sold.
2. Posting Entries to the General Ledger
Liability accounts represent what the
business owes to others. Common examples include accounts payable, which refers
to unpaid bills to suppliers, and loans payable,
which are outstanding amounts borrowed from banks or other lenders. Taxes payable covers taxes that
are due but haven’t been paid yet, while wages payable
represents salaries earned by employees that are still unpaid. These
liabilities increase when the business borrows money or delays payment, and
they decrease when those debts or obligations are settled.
3. Equity Accounts
Equity accounts show the owner’s claim or
stake in the business. These accounts reflect how much of the business truly
belongs to the owner after all debts are paid. Examples include Owner’s Capital, which is the
money the owner invests into the business, Owner’s
Drawings, which represents money withdrawn by the owner for
personal use, and Retained Earnings,
which are profits that are kept in the business rather than distributed. Equity
increases when the owner adds more funds or when the business earns a profit,
and it decreases when there are losses or when the owner takes money out of the
business.
4. Income Accounts
Income accounts, also known as revenue accounts, track the money a
business earns through its operations. Common examples include Sales Revenue, which is income
generated from selling products, Service Income,
which refers to money earned by providing services, and Interest Income, which includes
earnings from bank interest or other investments. These accounts increase as
the business brings in more revenue and serve as a key indicator of how well
the business is performing financially.
5. Expense Accounts
Expense
accounts show what the business spends to keep its operations running
smoothly. Some of the most common
expense accounts include Rent Expense, which covers the cost of office
or shop space, and Utilities Expense, which includes electricity, water,
internet, and other essential services. Salaries or Wages Expense
reflects the money paid to employees, while Office Supplies Expense
tracks spending on items like pens, paper, and software. Advertising Expense
covers marketing and promotional efforts to attract customers. These accounts
increase whenever the business incurs a cost and play a crucial role in
tracking where money is going and managing overall spending.
Key Takeaways
✅ Bookkeeping accounts help organize financial transactions for accurate recording and reporting
✅ Asset accounts track what the business owns—like cash, inventory, and equipment
✅ Liability accounts show what the business owes—such as loans, payables, and taxes
✅ Equity accounts represent the owner’s claim—capital invested, drawings, and retained earnings
✅ Income accounts record money earned from sales, services, or interest
✅ Asset accounts track what the business owns—like cash, inventory, and equipment
✅ Liability accounts show what the business owes—such as loans, payables, and taxes
✅ Equity accounts represent the owner’s claim—capital invested, drawings, and retained earnings
✅ Income accounts record money earned from sales, services, or interest
Write your awesome label here.
Access all Accounting and Bookkeeping Courses from One Portal.
Mastering Bookkeeping and Accounting
MBA simplifies accounting, ledger management, account balancing and financial statement preparation.
QuickBooks Online For Bookkeepers
From Beginner to Expert: Master QuickBooks Online. Effortlessly Navigate, Analyze Transactions, and Unlock its Full Potential.
Xero Accounting For Bookkeepers
Learn how to use Xero, the leading online accounting software to perform most of the essential bookkeeping tasks.
ChatGpt for Bookkeepers and Accountants
Learn how to use the ChatGPT prompt toolkit to simplify daily accounting tasks for accountants and bookkeepers instantly.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay informed with the latest accounting tips, tools, and updates from Accountutor right in your email inbox.
Thank you!
Policy Pages

Download QuickBooks Online PDF Guide
Thank you!

Download QuickBooks Online Cheat Sheet
Thank you!

Download ABCD of Accounting
Thank you!

Download Checklist 2024
Thank you!
Register For Free!
Thank you!
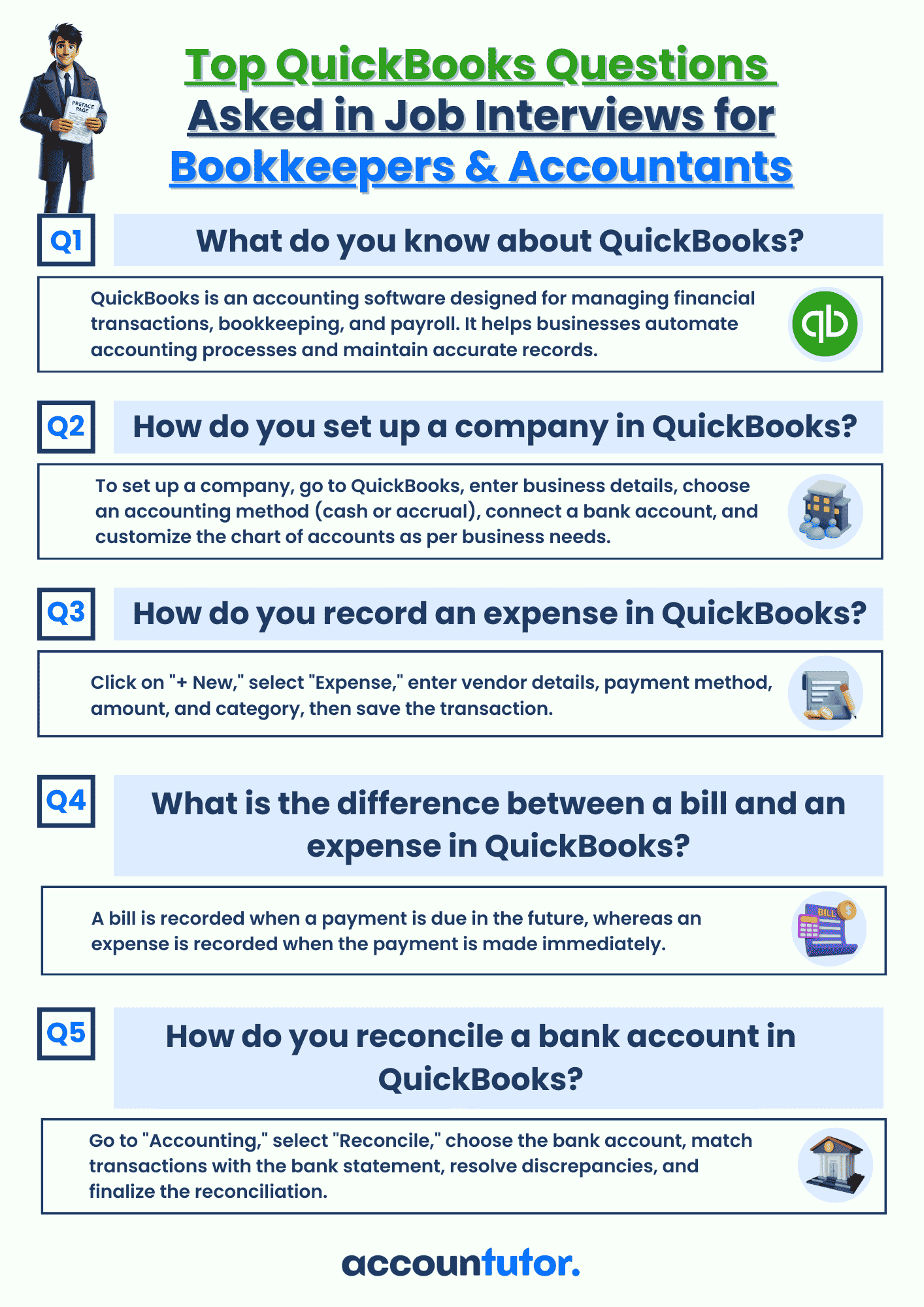
Download Interview Questions
Thank you!
Register for this webinar: How to Master QuickBooks Online— Without Feeling Overwhelmed
7th JUNE 2025 | 8:00 AM PST | 11:00 AM EST
Thank you! The joining link will be sent to your email shortly!
Webinar joining link will be sent to your email address.

Download QBO Job Interview Questions and Answers PDF
Thank you!

Download Interview Questions
Thank you!

Download 50 Interview Questions For Bookkeepers
Thank you!

Download QuickBooks Online Guidebook
Thank you!

