What is the Accounting Equation ?
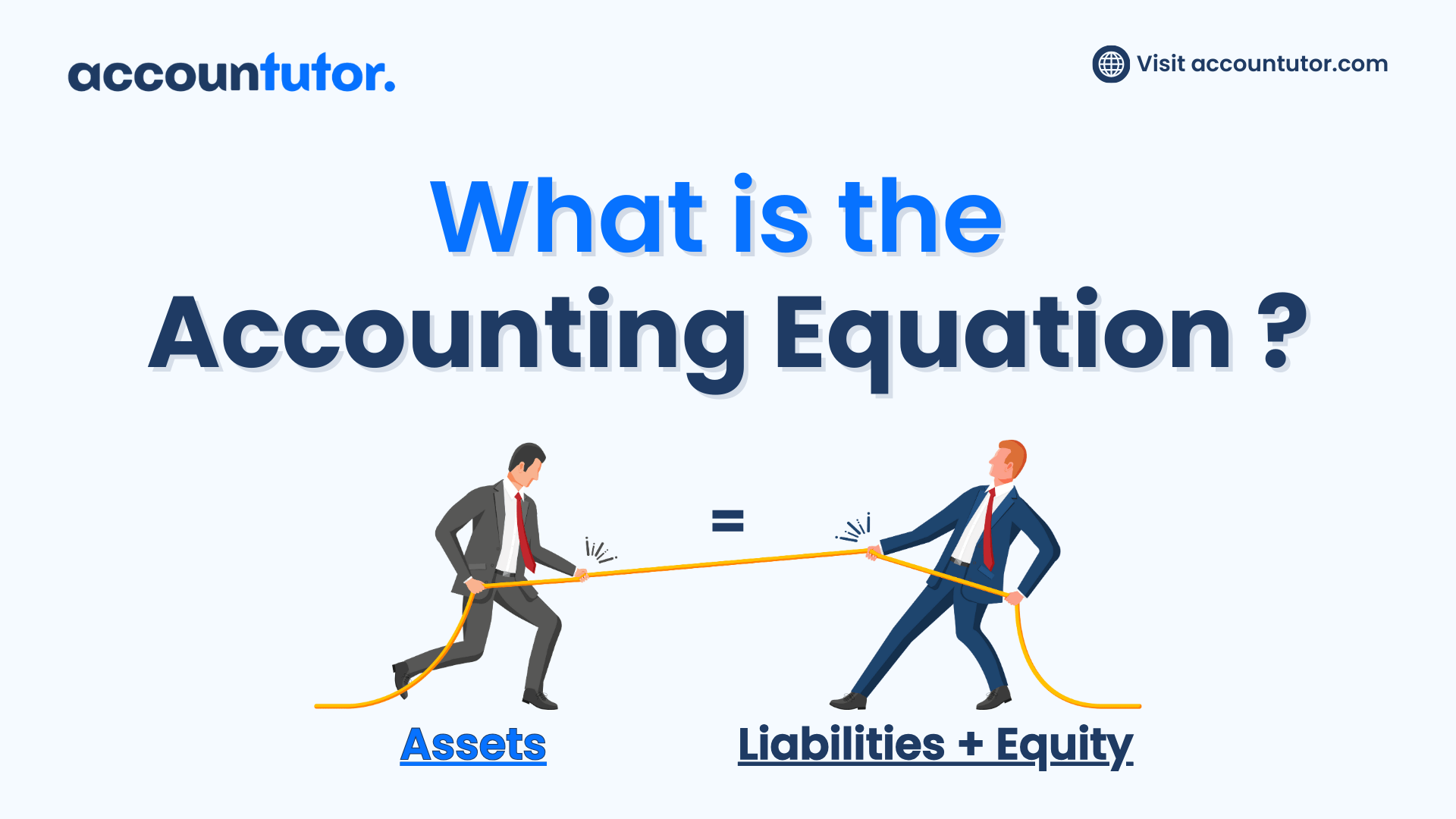
Ever wondered how your business’s financial transactions come together to keep everything balanced? The secret lies in one fundamental formula that drives the entire accounting system: The Accounting Equation. This simple yet powerful equation ensures that your financial records always stay in harmony. Let’s break it down!
What Is the Accounting Equation and Why Is It the Foundation of Accounting?
Assets=Liabilities+Equity
This fundamental formula, known as the accounting equation, serves as the backbone of double-entry bookkeeping and the basis for maintaining accurate financial records. It ensures that every financial transaction is recorded in a way that reflects the true financial position of a business.
But what exactly does this equation mean? Let’s break it down step by step.
Assets: These are all the resources a business owns that have value. This includes cash, equipment, inventory, accounts receivable, property, and more. Assets represent the things a business can use to operate or generate revenue.
Liabilities: These are the obligations or debts the business owes to others, such as loans, unpaid bills, or accrued expenses.
Equity: This represents the owner’s stake in the business after all liabilities have been paid. It includes the initial investment made by the owner(s) and any retained earnings accumulated over time.
In essence, the accounting equation shows that a company’s assets are financed by either borrowing money (liabilities) or through investments by the owners (equity). The equation’s balance ensures that financial records are accurate, reliable, and ready for analysis.
How Does the Accounting Equation Work?
Understanding how the accounting equation applies in real-world scenarios is crucial for mastering its principles. Let’s explore three examples that demonstrate its practical application.
Imagine you’re starting a coffee shop, and you contribute $10,000 of your own money to get the business up and running.
Here’s how the accounting equation works in this scenario:
Assets: Your business now has $10,000 in cash as a resource to operate.
Liabilities: Since the funds came from your personal investment and not from a loan, liabilities remain at $0.
Equity: The $10,000 you contributed is recorded as equity, representing the owner’s investment in the business.
The Accounting Equation:
Assets=Liabilities+Equity
$10,000=$0+$10,000
$10,000=$10,000
The equation balances perfectly, indicating that the business’s assets are fully funded by the owner’s equity.
Now, let’s say your coffee shop takes out a $5,000 loan to purchase additional equipment. How does this transaction affect the equation?
Assets: The loan increases cash by $5,000, bringing total assets to $15,000.
Liabilities: The loan creates a new obligation, increasing liabilities by $5,000.
Equity: Your initial $10,000 investment remains unchanged.
The Accounting Equation:
Assets=Liabilities+Equity
$15,000=$5,000+$10,000
$15,000 = $15,000
The equation remains balanced, showing that the additional assets are financed by the new liability.
Let’s take it a step further. You use $4,000 of your business’s cash to purchase equipment for the coffee shop.
Assets: Cash decreases by $4,000, but equipment increases by the same amount. The total assets remain $15,000, but their composition changes.
Liabilities: Stay at $5,000, as no new debts were incurred.
Equity: Remains $10,000, reflecting the owner’s unchanged stake in the business.
The Accounting Equation:
Assets=Liabilities+Equity
$15,000=$5,000+$10,000
This example illustrates that while the type of assets changes, the total value remains consistent, and the equation remains balanced.
Why is the Accounting Equation Important?
1. Ensures Accuracy in Financial Records
The accounting equation acts as a built-in error-checking mechanism. Every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring that the books remain balanced.
Example: If a transaction causes an increase in assets but doesn’t correspondingly affect liabilities or equity, it’s a clear sign of an error that needs correction.
2. Simplifies Financial Transactions The accounting equation provides a simple framework to record even the most complex financial transactions. By understanding how a transaction impacts assets, liabilities, and equity, accountants can accurately classify and record it.
3. Offers Insights into Financial Health
The accounting equation provides a snapshot of a business’s financial position. By analyzing the components of the equation, business owners and stakeholders can:
- Assess the level of debt compared to equity.
- Evaluate liquidity and solvency.
- Identify potential financial risks or opportunities.
Example:
A business with $100,000 in assets, $80,000 in liabilities, and $20,000 in equity is more leveraged (i.e., relies more on debt) than one with equal liabilities and equity, indicating higher financial risk.
The Role of the Accounting Equation in Financial Statements
1.Balance Sheet: The balance sheet is a direct representation of the accounting equation, showing the relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
2.Profit and Loss Statement (P&L): While the P&L focuses on income and expenses, it impacts the accounting equation by affecting the equity portion through retained earnings.
3.Cash Flow Statement: The cash flow statement reflects changes in assets (cash) resulting from operating, investing, and financing activities, tying back to the accounting equation.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
1. Forgetting Double-Entry Accounting: Omitting one side of a transaction results in an unbalanced equation. Always ensure that every transaction has both a debit and a credit entry.
2.Misclassifying Transactions: Placing liabilities under equity or vice versa can distort financial reports. Proper training and accounting software can help prevent this error.
3.Neglecting Adjustments: Failure to record accrued expenses or revenue leads to inaccuracies. Regularly review and update your records to reflect these changes.
Practical Tips for Mastering the Accounting Equation
1. Practice with Real-Life Scenarios:
Work through sample transactions to understand their impact on the equation.
2. Use Technology:
Accounting software like QuickBooks or Xero automates double-entry bookkeeping, ensuring that the accounting equation remains balanced.
3.Revisit the Basics:
If a transaction doesn’t make sense, go back to the equation:
Assets= Liabilities+Equity
Take Your Accounting Knowledge to the Next Level
Ready to learn more? Enroll in our free mini-course, ‘Accounting Explained,’ on Accountutor.com.
Our expert-led tutorials simplify accounting principles and provide practical examples to help you build confidence. From understanding the basics of bookkeeping to preparing financial statements, our courses are tailored to meet your needs.
Visit Accountutor.com today and take control of your financial future!
Conclusion
Start your journey today with Accountutor’s free resources and courses. Visit Accountutor.com now and transform your approach to financial management!
Accounting and Bookkeeping courses for you
Subscribe to our newsletter
Policy Pages




Register for this webinar: How to Master QuickBooks Online— Without Feeling Overwhelmed





