What is Hybrid Costing System?
Jan 20

Introduction
A hybrid costing system combines elements of both job costing and process costing to account for production costs in industries where products or services share characteristics of customized and standardized production. This system is used when certain parts of production are uniform and continuous (process costing) while other parts require customization (job costing). The hybrid system allows businesses to capture costs accurately across varied production stages and allocate them appropriately.
How it works?
A furniture manufacturer uses a hybrid costing system to track production costs. The company mass-produces wooden chair frames, which are identical and fall under process costing. However, customers often request customized upholstery, colors, or finishes, making this portion of production unique and suited to job costing. The hybrid system records the cost of raw materials, labor, and overhead for the standardized chair frames as process costs, while the additional costs for custom upholstery and finishes are tracked using job costing. This approach ensures accurate cost allocation, supporting pricing strategies and profitability analysis. A furniture manufacturer uses a hybrid costing system to track production costs. The company mass-produces wooden chair frames, which are identical and fall under process costing. However, customers often request customized upholstery, colors, or finishes, making this portion of production unique and suited to job costing. The hybrid system records the cost of raw materials, labor, and overhead for the standardized chair frames as process costs, while the additional costs for custom upholstery and finishes are tracked using job costing. This approach ensures accurate cost allocation, supporting pricing strategies and profitability analysis.
Why it is important?
The hybrid costing system is highly relevant for industries where production involves both standardized processes and customization, offering several advantages:
1. Accurate Cost Allocation: By combining process and job costing, the hybrid system ensures that costs are allocated precisely to different production stages, improving profitability analysis.
Example: A car manufacturer tracks assembly line costs as process costs while customizing features like paint color and interior finishes using job costing.
2. Flexibility in Diverse Operations: The system adapts to businesses that require both mass production and customization, making it ideal for industries with mixed production models.
Example: A bakery uses process costing for standard bread production and job costing for custom wedding cakes.
3. Improved Pricing Strategies: With detailed cost tracking, businesses can price their products or services more accurately based on production costs.
Example: A packaging company sets competitive prices for standard boxes while accounting for customization costs for branded packaging.
4. Enhanced Financial Reporting: The hybrid system provides detailed cost information that supports decision-making, financial analysis, and reporting requirements.
Example: A furniture manufacturer prepares financial reports showing separate costs for standardized frames and customized features, improving transparency.
Types of Applications for Hybrid Costing System:
1. Manufacturing Industry: Used where standardized production meets customer-specific requirements.
Example: An electronics company uses process costing for circuit boards and job costing for custom-built computers.
2. Automotive Industry: Applied when vehicles are assembled using standardized processes but customized with features like color or accessories.
Example: A car manufacturer produces standard car models on an assembly line and customizes seats, paint, and add-ons based on customer orders.
3. Service Industry: Used when services involve both standardized workflows and unique customer needs.
Example: A software development company tracks the cost of standard coding practices as process costs and additional client-specific requirements as job costs.
4. Retail and Apparel Industry: Combines process costing for mass-produced garments and job costing for customized designs.
Example: A clothing manufacturer produces basic T-shirts in bulk while offering custom printing options tracked through job costing.
Conclusion:
The hybrid costing system is an effective cost accounting approach for industries requiring a mix of standardized and customized production processes. By integrating elements of job and process costing, this system ensures precise cost tracking, supports informed decision-making, and enhances financial transparency. Businesses in manufacturing, automotive, service, and retail sectors can leverage hybrid costing to optimize pricing strategies, manage diverse operations efficiently, and achieve long-term profitability.
Accounting and Bookkeeping courses for you
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay informed with the latest accounting tips, tools, and updates from Accountutor right in your email inbox.
Thank you!
Policy Pages

Download QuickBooks Online PDF Guide
Thank you!

Download QuickBooks Online Cheat Sheet
Thank you!

Download ABCD of Accounting
Thank you!

Download Checklist 2024
Thank you!
Register For Free!
Thank you!
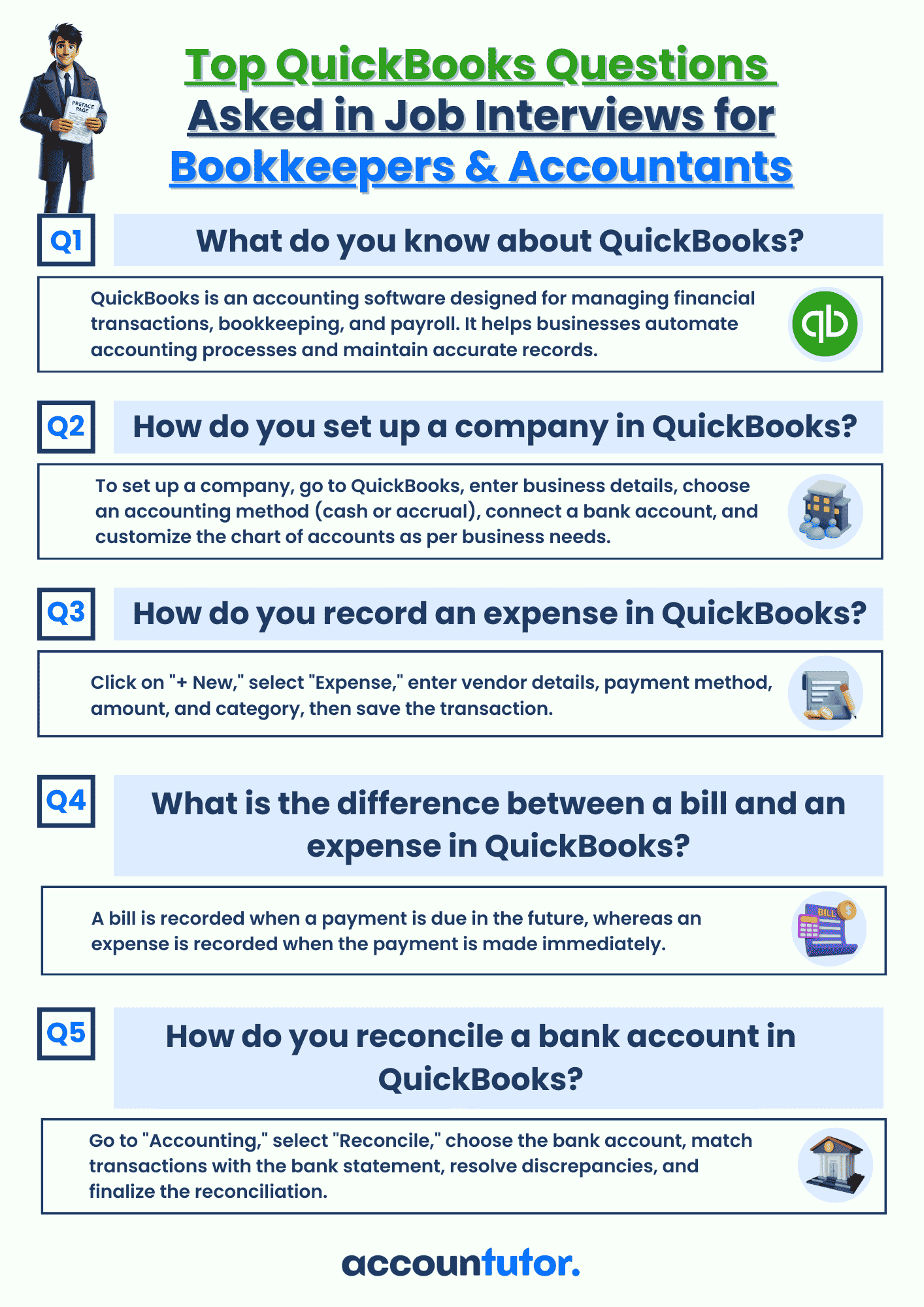
Download Interview Questions
Thank you!
Register for this webinar: How to Master QuickBooks Online— Without Feeling Overwhelmed
7th JUNE 2025 | 8:00 AM PST | 11:00 AM EST
Thank you! The joining link will be sent to your email shortly!
Webinar joining link will be sent to your email address.

Download QBO Job Interview Questions and Answers PDF
Thank you!

Download Interview Questions
Thank you!

Download 50 Interview Questions For Bookkeepers
Thank you!

Download QuickBooks Online Guidebook
Thank you!

