What is FIFO (First In, First Out)?
Dec 25

Introduction
FIFO, or First In, First Out, is an inventory valuation and cost management method where the oldest inventory (first purchased or produced) is sold or used first. This approach ensures that the cost of older items is matched with current revenue, while newer inventory remains in stock. FIFO is particularly beneficial in industries dealing with perishable or time-sensitive goods and is widely recognized for its simplicity and alignment with the natural flow of inventory.
How it works?
A supermarket uses FIFO to manage its stock of yogurt. On February 1, it purchases 500 tubs of yogurt at $2 each. On February 10, it buys another 500 tubs at $3 each. By February 20, it sells 800 tubs. Using the FIFO method, the cost of the first 500 tubs sold is $2 each, while the cost of the next 300 tubs sold is $3 each. The cost of goods sold (COGS) is $2,300 (500 × $2 + 300 × $3), and the remaining inventory value is $600 (200 × $3). FIFO ensures that older yogurt is sold first, reducing the risk of spoilage and ensuring accurate cost matching.
Why it is important?
FIFO is a vital inventory management method, with applications that benefit businesses across various sectors:
1. Accurate Cost Matching: FIFO ensures that the cost of goods sold reflects the price of older inventory, providing an accurate representation of profitability.
Example: A bakery matches the cost of flour purchased last month to its current bread sales, ensuring transparency in profit calculations.
2. Minimized Waste and Obsolescence: FIFO reduces the risk of holding expired or outdated inventory by prioritizing the sale of older stock.
Example: A pharmaceutical company rotates medications using FIFO to ensure older batches are dispensed before expiration.
3. Logical and Easy to Implement: FIFO aligns with the physical movement of goods in many industries, making it intuitive and straightforward to apply.
Example: A grocery store naturally sells older produce first, following FIFO principles without additional effort.
4. Higher Net Income During Inflation: In times of rising prices, FIFO uses lower-cost inventory for COGS, resulting in higher net income.
Example: A retailer sees increased profits by selling products at current prices while accounting for older, lower-cost inventory.
Types of Situations Where FIFO is Used (Expanded Explanation with Examples):
1. Perishable Goods: FIFO is essential for industries dealing with goods that have limited shelf lives, such as food and beverages. By selling older items first, businesses reduce waste and ensure product freshness.
Example: A bakery uses FIFO to sell day-old bread before freshly baked loaves to minimize spoilage and maintain quality.
2. Retail Industry: In retail, FIFO helps manage seasonal inventory and prevent obsolescence. Retailers sell older items first to clear stock and make room for new products.
Example: A clothing store uses FIFO to sell winter jackets from last season before introducing the latest designs.
3. Manufacturing: Manufacturing businesses use FIFO to manage raw materials and maintain production continuity. Older materials are consumed first, preventing wastage and ensuring product consistency.
Example: A furniture manufacturer uses wood from earlier deliveries before newer batches to maintain inventory flow.
4. Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare: FIFO is critical in managing medications and healthcare supplies to avoid expiration and ensure patient safety.
Example: A hospital pharmacy dispenses older vaccines first to minimize waste and meet regulatory compliance.
5. Warehousing and Logistics: Warehouses use FIFO to optimize inventory turnover and maintain stock freshness. Goods are stored and shipped in the order they arrive.
Example: A logistics company ships older packages first, ensuring efficient inventory rotation and reducing the risk of stock sitting idle.
6. Technology Products: FIFO is used to manage rapidly depreciating inventory, such as electronic gadgets, where older models lose value quickly.
Example: An electronics retailer prioritizes selling older smartphone models before new releases to avoid markdowns.
Conclusion:
FIFO is a practical and efficient inventory management method that aligns with the natural flow of goods in many industries. By prioritizing the sale of older inventory, FIFO minimizes waste, ensures accurate cost reporting, and supports better financial decision-making. Whether in retail, manufacturing, or healthcare, FIFO provides businesses with a reliable approach to inventory control, enhancing profitability and operational efficiency.
Accounting and Bookkeeping courses for you
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay informed with the latest accounting tips, tools, and updates from Accountutor right in your email inbox.
Thank you!
Policy Pages

Download QuickBooks Online PDF Guide
Thank you!

Download QuickBooks Online Cheat Sheet
Thank you!

Download ABCD of Accounting
Thank you!

Download Checklist 2024
Thank you!
Register For Free!
Thank you!
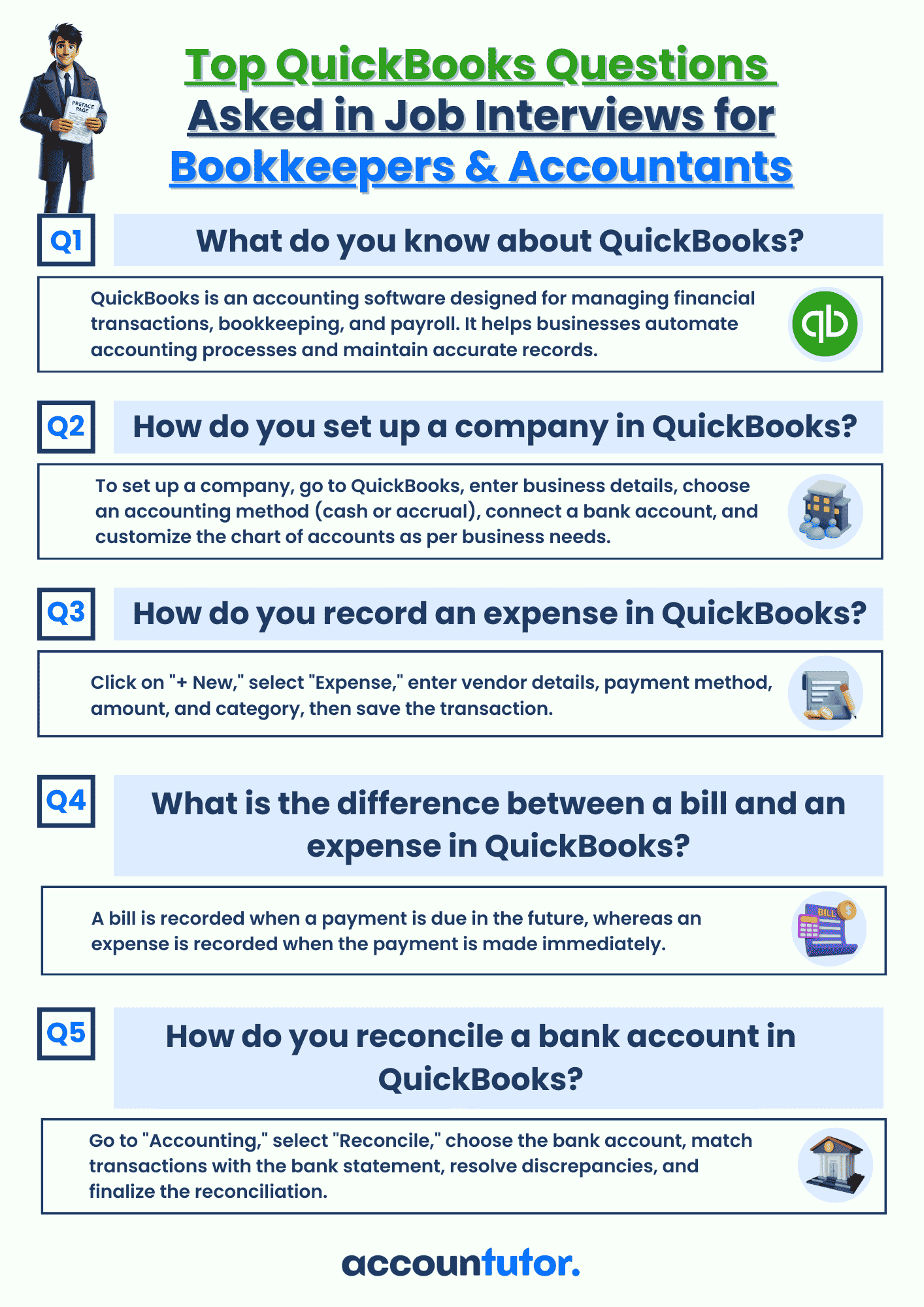
Download Interview Questions
Thank you!
Register for this webinar: How to Master QuickBooks Online— Without Feeling Overwhelmed
7th JUNE 2025 | 8:00 AM PST | 11:00 AM EST
Thank you! The joining link will be sent to your email shortly!
Webinar joining link will be sent to your email address.

Download QBO Job Interview Questions and Answers PDF
Thank you!

Download Interview Questions
Thank you!

Download 50 Interview Questions For Bookkeepers
Thank you!

